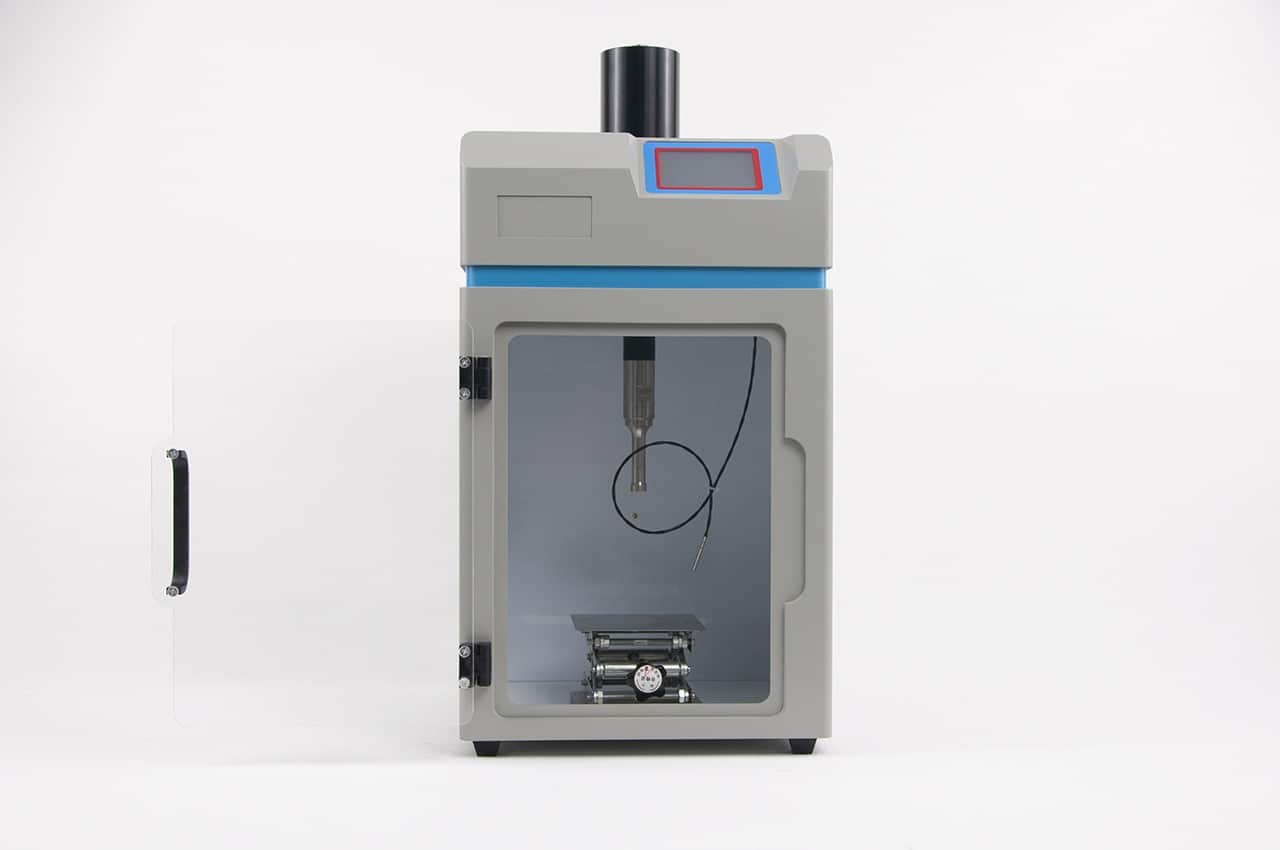
The primary difference between sonication and homogenization lies in the methods they employ to disrupt cell structures.
Sonication:
Sonication is a cell disruption technique that involves the application of high-frequency sound waves or ultrasonic energy to break cells. The use of sound energy in sonication causes the disruption of tissues and cells. It is especially effective for breaking down bacteria, yeasts, fungi, algae, and mammalian cells. Sonication generates a substantial amount of heat, necessitating its operation under cooled conditions, often by immersing the sample in an ice bath. It is particularly suited for samples with volumes below 100 mL and is executed using a device called a sonicator.
Homogenization:
Homogenization, on the other hand, is a cell disruption method that predominantly employs physical force to break cell membranes. This method involves various techniques such as mechanical homogenization, bead homogenization, and grinding. Mechanical homogenization uses a homogenizer, while bead homogenization uses glass or metal beads to gently abrade cells. Grinding involves the use of a mortar and pestle, often in conjunction with freezing the sample using liquid nitrogen.
Key Differences:
- Sonication primarily utilizes sound energy to disrupt cells, whereas homogenization relies on physical force to break cell membranes.
- Sonication is faster than homogenization in lysing cells.
- Sonication generates more heat, requiring cooling measures during the process, while homogenization may involve freezing the sample with liquid nitrogen in grinding.
- Sonication is best suited for smaller sample volumes (below 100 mL), whereas homogenization techniques can be applied to larger volumes.
- Sonication employs a sonicator, while homogenization involves different equipment such as a homogenizer, beads, or a mortar and pestle.
Both methods are physical cell disruption techniques, and while effective, they can potentially lead to protein denaturation and aggregation. Additionally, the reproducibility of results may vary in both techniques.
This distinction between sonication and homogenization is crucial in laboratory settings where cell disruption techniques are essential for various analytical purposes.
If you want to buy, please click here!